1 Which of Following Cells Are Targeted by Hiv
As the major targets for HIV T helper cells CD4 T cells Fig. Human MAIT cells sit at the interface between innate and adaptive immunity are polyfunctional and are capable of killing pathogen infected cells via recognition of the Class IB molecule MR1.
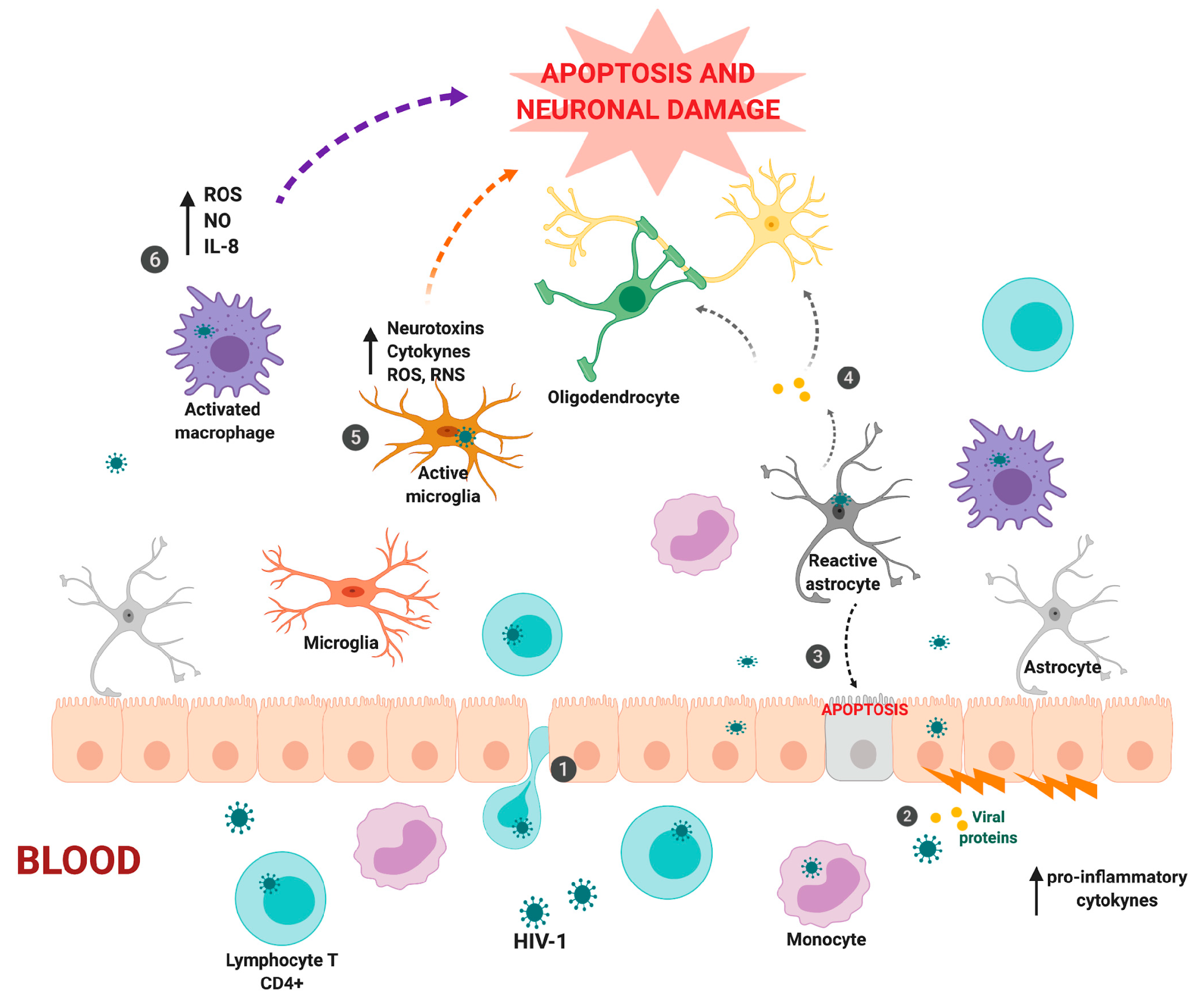
Cells Free Full Text New Challenges Of Hiv 1 Infection How Hiv 1 Attacks And Resides In The Central Nervous System Html
UCLA researchers presented today the first case of a US.
. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 HIV-1 infects and kills immune cells known as CD4 T cells leading to the disease AIDS. α-Langerin mAb targeted splenic CD8 DCs selectively in vivo whereas α-DEC205 and α-Clec9A mAbs targeted additional cell types. Resting CD4 T cells are known to be the principal reservoir of HIV but we have now abundant proofs that many other cell reservoirs such as hematopoietic stem cells dendritic cells microglial cells and cells from the monocyte-macrophage lineage reviewed in 123 exist.
CD4 T Cells. Abstract Disruption of CCR5 or CXCR4 the main human immunodeficiency virus type 1 HIV-1 co-receptors has been shown to protect primary human CD4 T cells from HIV-1 infection. However direct versus indirect reductions of these T cells within HIV.
BackgroundHumanimmunodeficiencyvirus type 1 HIV-1 is a lentivirus andshares withothermembers of this retroviral subfamily the ability to replicate in nondividingcells in particular cells of the monocyte macrophage lineage. This feature relies on the pres-ence of a specific nuclear localization signal NLS within the viral matrix protein. T-cells and LCs are the first cells targeted by HIV-1 during early viral exposure of the inner foreskin.
HIV can infect a variety of immune cells such as CD4 T cells macrophages and microglial cells. MAIT cells have recently been shown to possess an antiviral protective role in vivo and we therefore sought to explore this in relation to HIV-1 infection. Which of the following cells are primarily targeted by HIV.
Base editing can install targeted point mutations in cellular genomes and can thus efficiently inactivate genes by introducing stop codons or eliminating start codons without double-stranded DNA. HIV-1 entry to macrophages and CD4 T cells is mediated through interaction of the virion envelope glycoproteins gp120 with the CD4 molecule on the target cells membrane and also with chemokine co-receptors. However macrophages B cells monocytes and other.
HIV-1-pulsed dendritic cells efficiently transmit HIV-1 to cocultured CD4 T cells Wu. Here we directly examine how cell-free and cell-to-cell infections differ from infections initiated with cell-free virus in the number of genetic copies. Current drug treatments enable HIV-1 infected patients to live relatively long and healthy lives.
Ad We Know What It Takes To Help Stop The Virus - Learn About HIV Treatment. This study provides new insights into activators of HIV latency and it also provides compelling evidence for a novel HIV eradication strategy. First the massive entry of viral particles into target cells across the virological synapse has been shown to be responsible for caspase-1-mediated pyropoptosis of target T cells 71.
Innate immune cells eg dendritic cells and natural killer cells are the first line of defence which HIV encounters upon entry to the body. Zation of microbial-specific T cells from the polyclonal repertoire using HIV gag-p24 protein as an antigen. Besides these cellular reservoirs HIV-1 can persist latently in.
During cell-to-cell transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 HIV-1 many viral particles can be simultaneously transferred from infected to uninfected CD4 T cells through structures called virological synapses VS. Total DNA in CD4 T cells at day 876 after transplantation was undetectable in all replicates by ultra-sensitive qPCR. Woman living with HIV-1 that is in remission after she received a new combination of specialized stem cell transplants for treatment of acute myeloid leukemia AML.
It is noteworthy to mention that cell-to-cell transfer of HIV-1 between T cells is associated to an increase mortality of the target cells when compared with cell-free infection of T cells. Critical unmet challenges are to determine whether bnAb precursor naïve B cells bind germline-targeting immunogens and occur at sufficient frequency in humans for reliable. The present study demonstrates that PKC412 potently activates HIV-1 latency from the HIV-1 latently infected ACH2 cell line and primary resting CD4 T cells by activating the NF-κB pathway.
When the mAb heavy chains were engineered to express gag-p24 the α-Langerin. The PSGL-1 level is greatly up-regulated during inflammation. The recovery of CD4 count was slow.
Here we found that PSGL-1 and CD43 expression inhibits HIV spreading infection. HIV-1-infected cells affect specific chemokines secretion by the inner foreskin. For this reason in recent years a substantial effort has been put to identification of druggable host cell factors that are involved in HIV-1 replication.
An attractive way to target HIV-1 life cycle that may be less sensitive to viral mutagenesis is the direct targeting of host cell factors that are utilized by the virus. PSGL-1 and CD43 are surface glycoproteins expressed on blood CD4 T cells to bind to selectins for T cell tethering rolling and migration into inflamed tissues. Furthermore some of these reservoirs are found in sanctuaries such as the genital tract the.
Moreover HIV -1 specific CD8 and CD4 T-cell responses remained absent in the 24 months following therapy. This is hypothesized to be a result of treatment with. We have previously shown that LCs attracted to the epidermal compartment of foreskin tissue by HIV-1-infected cells were the first immune cell targeted by HIV-1.
HIV Targets T Cells. 1 are the most recognized and studied immune cells in HIV researchDepletion of these important immune cells is the hallmark of HIV infection 18 and contributes to the symptomatic manifestation that characterizes AIDS 19. Tissue macrophages are one of the target cells for HIV.
HIV-1 persists in all subsets of memory CD4 T cells as well as a subset of functional T cells such as T follicular helper cells T regulatory cells Th1 cells and Th17 cells 6. The oral abstract was presented at CROI 2022 the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections. These macrophages harbour the virus.
Germline-targeting immunogens aim to initiate bnAb induction by activating bnAb germline precursor B cells. T cells are the main target of HIV in the blood and they act as the host that the virus needs in order to replicate. The motility of these migratory cells dependents on environmental cues such as chemokines and cytokines secreted by the tissue.
Induction of broadly neutralizing antibodies bnAbs is a major HIV vaccine goal.

How Hiv Affects The Body Hiv Transmission Disease Progression More

Hiv Resistant And Hiv Specific Car Modified Cd4 T Cells Mitigate Hiv Disease Progression And Confer Cd4 T Cell Help In Vivo Molecular Therapy

Human Immunodeficiency Virus Hiv British Society For Immunology

Evolution During Primary Hiv Infection Does Not Require Adaptive Immune Selection Pnas
This Hiv Aids Specialist Explains Its Similarities And Differences To Covid 19
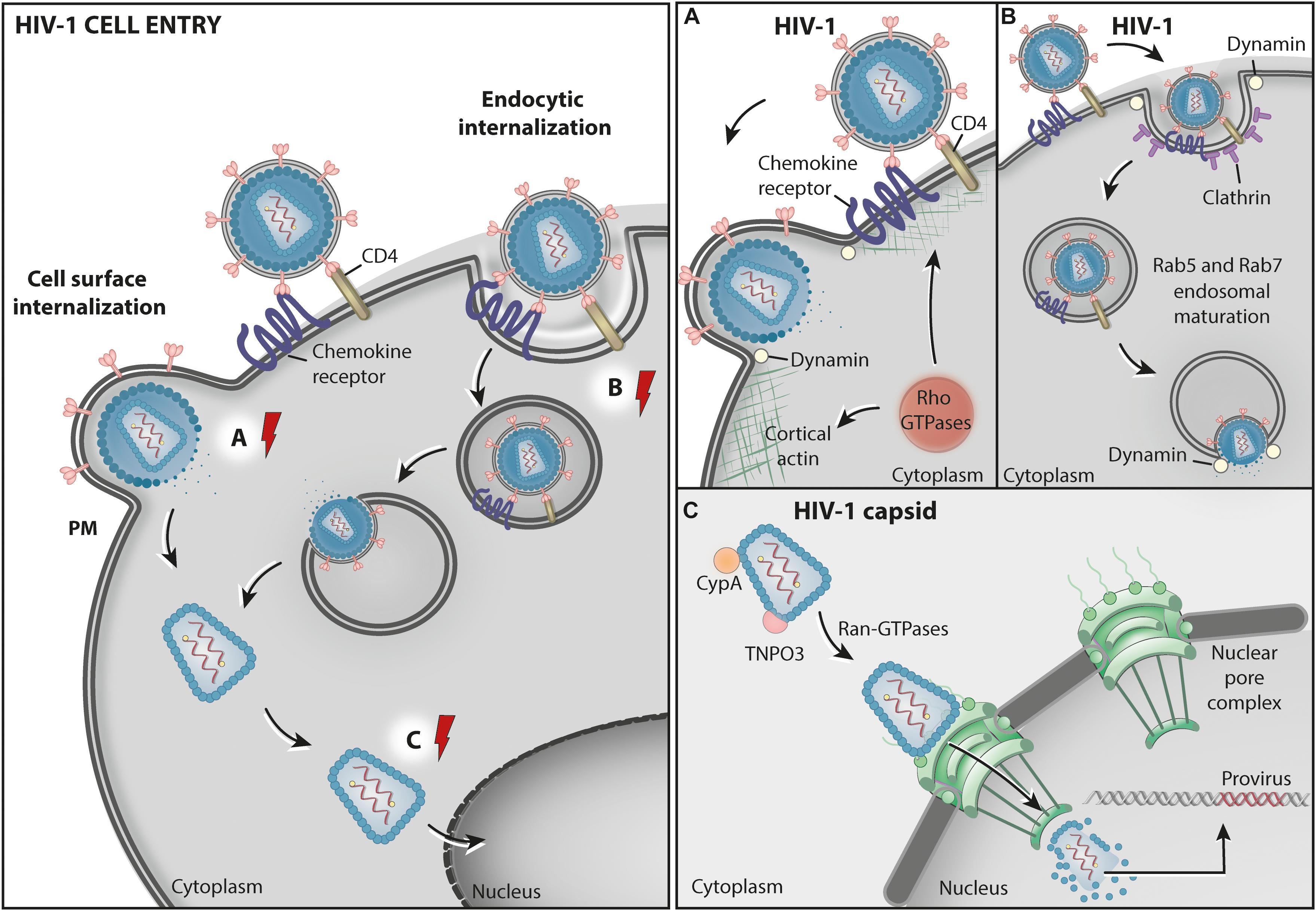
Frontiers Hiv 1 Hijacking Of Host Atpases And Gtpases That Control Protein Trafficking Cell And Developmental Biology
Innate Resistance To Hiv Through Natural Killer Cells

Human Immunodeficiency Virus Hiv British Society For Immunology

Ucla Led Team Refines Kick And Kill Strategy Aimed At Eliminating Hiv Infected Cells Ucla

Preventive And Therapeutic Features Of Broadly Neutralising Monoclonal Antibodies Against Hiv 1 The Lancet Hiv
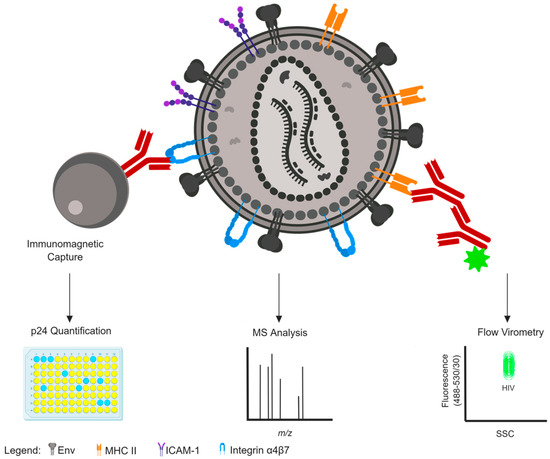
Viruses Free Full Text The Incorporation Of Host Proteins Into The External Hiv 1 Envelope Html

Pin On Mass Spectrometry Articles
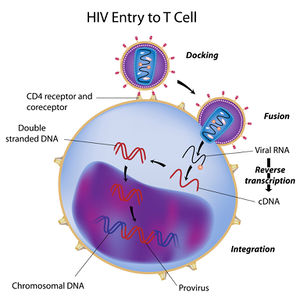
Hiv Aids In The U S Microbewiki

Viral Reservoirs In Elite Controllers Of Hiv 1 Infection Implications For Hiv Cure Strategies Ebiomedicine

Human Immunodeficiency Virus Hiv British Society For Immunology




Comments
Post a Comment